Crucial Gaps in Climate Risk Assessment Methods

A recent study co-authored by Stefano Battiston published in Nature Communications has identified critical shortcomings in the way climate-related risks to corporate assets are currently assessed.
Many current estimates of climate physical climate risk rely on simplified and proxy data that do not accurately represent a company’s true risk exposure. This can lead to significant underestimates of climate-related losses, with serious implications for business investment planning, asset valuation and climate adaptation efforts.
Potential losses up to 70% higher than previously estimated

The research team developed a new methodology that uses detailed information about the location and characteristics of a company’s physical assets, such as factories, equipment and natural resources. This approach provides a more accurate picture of climate risks than methods that use proxy data, which often assume that all of a company’s assets are located at its headquarters.
"When we compared our results with those using proxy data, we found that the potential losses from climate risks could be up to 70% higher than previously thought," says Stefano Battiston. "This underscores the critical need for more granular data in risk assessments."
Preparing for the worst: The role of extreme events
The authors also point to the importance of considering "tail risk" in climate assessments. Tail risk refers to the possibility of extreme events that, while rare, can have catastrophic impacts. "Many assessments focus on average impacts. Our research shows that the potential losses from extreme events can be up to 98% higher than these averages suggest," says Stefano Battiston. "Failure to account for these possibilities can leave businesses and investors dangerously unprepared."
More funding for climate adaptation
The study's findings have significant implications for climate policy, business strategy, and investment decisions. The researchers emphasize that more accurate risk assessments are crucial for developing effective climate adaptation strategies and determining appropriate levels of climate-related insurance and funding. "Our work shows that we may be seriously underestimating the financial resources needed for climate adaptation," concludes Stefano Battiston.
Multi-stage assessment process
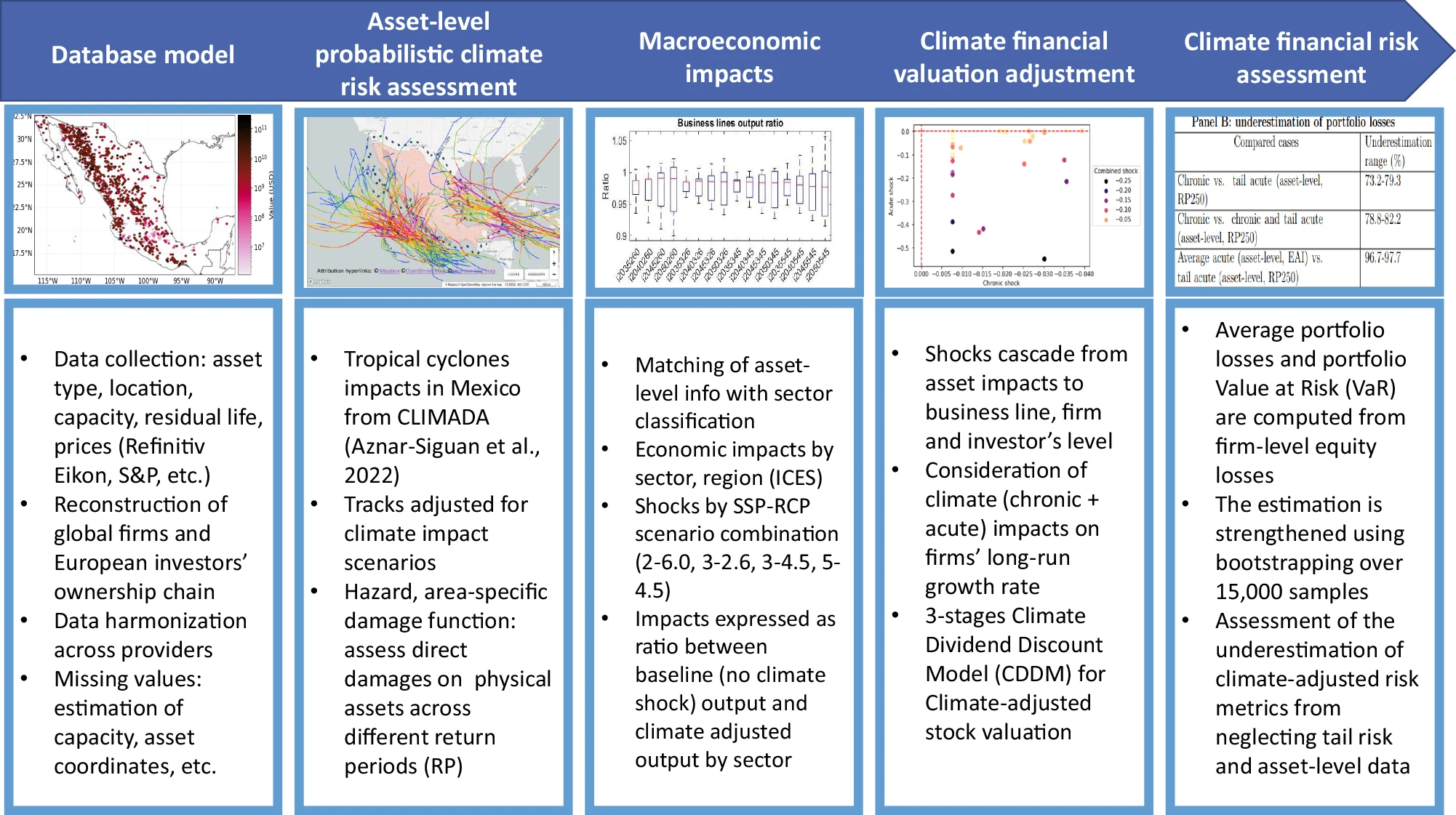
The blocks represent steps of implementation. Starting with asset-level data collection and harmonization the researchers feed an asset-level probabilistic risk assessment for tropical cyclones. Then, they computed the sector-based and macroeconomic impacts of physical risk using the Intertemporal Computable Equilibrium System (ICES) macroeconomic model. By combining climate impacts at the asset level and the resulting macroeconomic impacts, they could quantify the climate financial impacts at the firm level. Finally, they adjusted the financial valuation for equity contracts of the firm that owns the plants and computed the resulting adjustment in financial risk for the firm’s investor.
Learn more
Giacomo Bressan, Anja Duranovic, Irene Monasterolo, Stefano Battiston. Asset-level assessment of climate physical risk matters for adaptation. Nature Communications, 1 July 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48820-1
